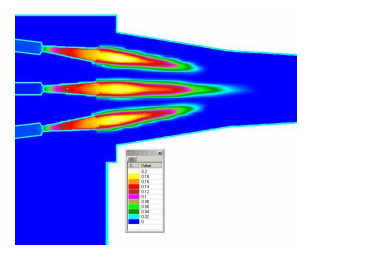
Due to a current trend of increasing rotational speed and power, the problem of tone noise and pressure pulsation in centrifugal ventilators becomes a more urgent issue. Often the level of tones determines noise characteristics; mainly these are blade-passing frequencies (BPF).

An approach for solving Fluid Structure Interaction in aerospace application is presented in this paper. The proposed approach is based on the two-way coupling between CFD code FlowVision and FEA code ABAQUS. The codes are coupled directly without using any 3rd party software or intermediate
structure.
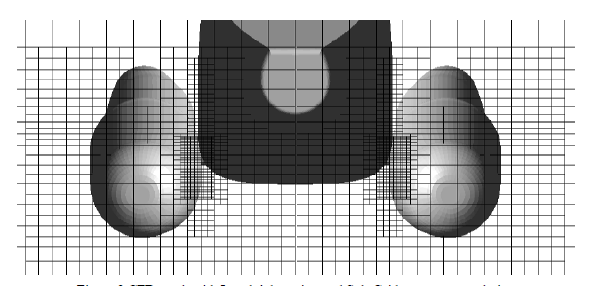
The description of the variable pitch propeller (VPP) is presented. An insight into this propeller operation is given. It's advantages which give the improvement of propulsion of different purpose ship in comparison with the traditional propeller are noted. To be said in the report it is confirmed by example.

The proposed fluid-structure interaction (FSI) approach is based on a two-way coupling between finite-element code Abaqus and finite-volume code FlowVision. The FSI simulation is possible due to a unique mesh generation method used in FlowVision.
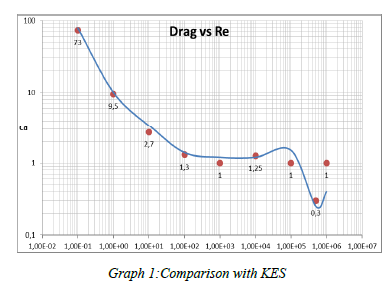
CFD analysis of flow over a cylinder for different Reynolds Numbers is explained in this paper by using different turbulence models.
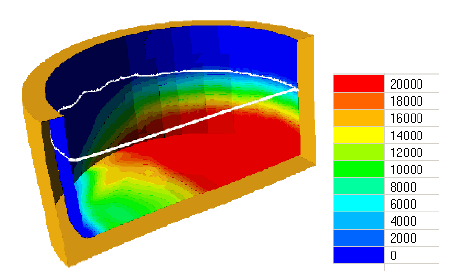
During operation of vertical cylindrical tanks for storage of oil and oil products significant quantities of compacted sediments can be formed and accumulated. As a result, tank useful capacity, tank farm turnover are reduced, oil storage cost is increased due to the
necessity to put tanks out of operation and perform their cleaning.
Feeder is one of the airships of the Multibody Advanced Airship for Transport (MAAT) system, under development within the EU FP7 project. MAAT is based on a modular concept composed of two different parts that have the possibility to join; respectively they are the so-called Cruiser and Feeder, designed on the lighter than air principle.

In order to supply tools for low noise design to the manufacturers of lawnmowers CETIM has set up a research project on blade noise (which is predominant on medium size and big machines). Experimental studies are based on the use of a special test rig which allows to measure blade noise without disturbances from the drive unit and to determine simultaneously the pressure fluctuations generated by the blade.
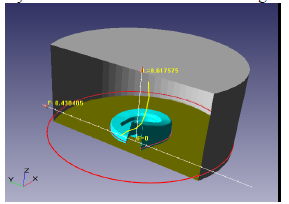
The paper presents a numerical simulation of the drop test in a still water for the multi-component box structure. The complexity of the problem is in the strong fluid-structure interaction (FSI) between the box and the water free surface. The numerical simulation of the drop test is performed with two software tools: Abaqus and FlowVision through the direct coupling interface, which manipulates, on the Abaqus side the Lagrangian finite-element mesh and on the FlowVision side the Eulerian finite-volume mesh with subgrid geometry resolution.

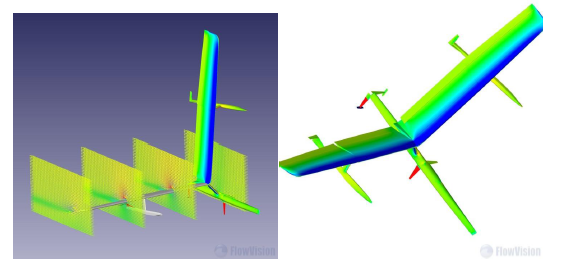
The brief for the boat, v-39 Albatross is to set a new world outright sailing speed record at Portland Harbor, UK by 2013. The boat is configured to add at least 10 knots to the current record by setting a speed above 65 knots (120 km/h). At speed the boat hulls will fly above the surface using a wing in ground effect. The pilot is able to sail on both port and starboard tack and can actively control the craft in speed, roll and height as well as direction.
The centrifugal pump of high specific speed with a diagonal type of impeller flow is studied experimentally and numerically. 2D and 3D numerical methods are used with applying acoustics – vortex equations.

Computational results of 3D turbulent compressible gas flow in a single-nozzle ejector are compared with experimental data. Full Navier-Stokes equations and k- model of turbulence are used for mathematical model of gas flow. In computations the suction gas flow rate was determined and compared with experimental one. Two computational grids – coarse and fine are used to perform simulation.